
Upselling Techniques are not about pushing people to buy things they do not want. At their best, they help customers make better decisions by showing options they might have missed. When done right, upselling feels helpful, not salesy. It increases average order value while improving the overall buying experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Upselling strategies works best when it feels helpful, not pushy, by guiding customers toward better choices they might have missed.
- Buyer psychology matters more than tactics; timing, framing, and ease of decision drive results.
- High-intent moments like checkout and post-purchase are ideal for upsells because resistance is already low.
- Clear value framing through tiers, bundles, and volume offers makes higher options feel logical, not expensive.
- Simplicity wins; confusing or irrelevant upsells quickly kill conversions.
- Personalization and social proof build trust and reduce hesitation, especially for service-based upsells.
- The strongest upselling techniques increase order value while improving the overall buying experience, not interrupting it.
The key is understanding how people actually make purchase decisions. Buyers are not always logical. They move fast, rely on mental shortcuts, and respond to how choices are presented. That is where smart Upselling Techniques make a real difference.
Table Of Contents
- Why Upselling Techniques Works
- Upselling Techniques To Increase Average Order Value
- Real-Life Examples of Upselling Techniques
- Conclusion
(Jump to the section that interests you the most!)
Why Upselling Techniques Works: A Buyer Psychology Perspective
Before jumping into tactics, it helps to understand why upselling works in the first place.
- Decision momentum: Once a customer decides to buy, their resistance drops. They have already crossed the hardest mental barrier. Upselling techniques work best when they build on this momentum instead of interrupting it.
- Loss aversion: People dislike missing out more than they enjoy gaining something extra. Framing an upsell as avoiding a loss often works better than framing it as an added benefit.
- Choice framing: How options are presented influences what feels like the right choice. A well-framed upsell makes the higher option feel logical, not excessive.
- Cognitive ease: The easier it is to understand and accept an upsell, the more likely it is to work. Confusing offers kill conversions. Clear upselling techniques reduce thinking effort.
9 Upselling Techniques To Increase Average Order Value
High-Intent Techniques (Customer Already Decided)
These Upselling Techniques work best when the customer has already made the decision to buy. Resistance is low, so the goal is to add value without slowing them down.
1. Product upgrades with One Click Upsell
Product upgrades are one of the most effective Upselling Techniques because they build on an existing decision. The customer already wants the product. Showing a better version with clear benefits makes the upgrade feel logical.
One-click acceptance matters here because it removes effort and doubt. When the upgrade is positioned as a smarter choice rather than a bigger spend, buyers are more likely to say yes.
Example: “Upgrade to the Pro version for advanced analytics with one click.”
2. Checkout upselling
Checkout upselling works because the buyer is already mentally committed. At this stage, customers are focused on completing the purchase, not rethinking it. Relevant addons that enhance the main product fit naturally into this moment.
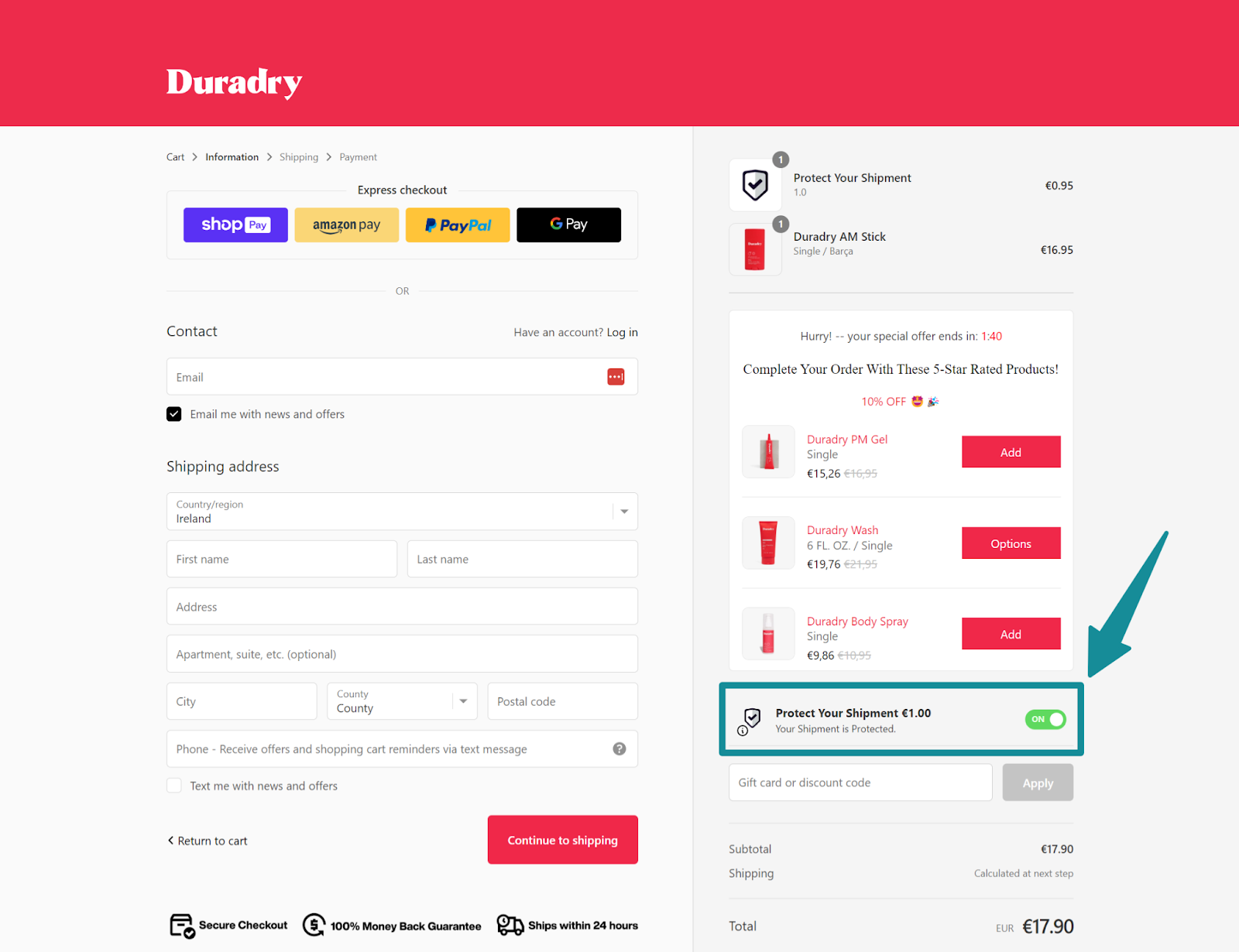
[Image Source: Upsell.com]
Example: “Add a screen protector for better durability before completing your order.”
3. Post-purchase upselling
Post-purchase upselling happens after the order is confirmed, when buyer anxiety is gone. Customers often feel satisfied and open to small additions that complete their purchase.
Because the main decision is already made, this upsell feels separate and low risk. When framed as a useful follow-up rather than another sale, acceptance rates are often high.
Example: “Add extended support coverage within 24 hours of your purchase.”
4. Feature-based upselling
Feature-based upselling strategies focuses on what the customer gets, not what they pay. Instead of pushing a higher price, it highlights missing features that solve specific problems.
This helps customers justify the upgrade on practical grounds. When the value is clear and tied to real use cases, the upsell feels like a better fit rather than an unnecessary expense.
Example: “Unlock automated reports and priority access with the premium plan.”
Psychology at work: These Upselling Techniques rely on commitment bias and reduced friction. Once customers commit, they want consistency in their choices. The sunk-cost fallacy also plays a role, since buyers are more willing to add value after investing time and money.
Value-Framing Techniques (Customer Comparing Options)
These Upselling Techniques work when customers are still evaluating their choices and trying to understand what offers the best value.
5. Tiered pricing
Tiered pricing simplifies decision-making by presenting clear options side by side. Instead of asking whether to buy, customers choose which version fits them best.
The middle or higher tier often feels like the safest choice because it balances cost and value. This framing makes higher-priced options feel reasonable rather than excessive.
Example: “Basic, Plus, and Premium plans displayed side by side.”
6. Bundling
Bundling groups related products or features into a single offer. This reduces the mental effort of choosing multiple items separately. Customers often perceive bundles as better value, even if the savings are modest.
![[Image Source: Upsell.com]](https://wpswings.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/bundling-upselling.png)
When done well, bundling positions the upsell as a complete solution instead of an add-on.
Example: “Buy the camera with a case and memory card as a bundle.”
7. Volume-based upselling
Volume-based upselling strategies encourages customers to buy more by showing clear advantages for higher quantities. This works especially well for repeat-use products.
The customer starts thinking in terms of long-term savings instead of immediate cost. It shifts the decision from spending more now to avoiding future purchases later.
Example: “Buy 3 months’ supply and save 15 percent.”
Psychology at work: Anchoring sets a reference point for pricing. Price relativity helps customers compare options more easily. Perceived savings reduce hesitation and make higher-value choices feel justified.
Personalization & Trust-Based Techniques
These Upselling Techniques are most effective when the buyer cares about relevance and reassurance more than discounts.
8. Personalized recommendations
Personalized recommendations use customer behavior, history, or context to suggest relevant products or upgrades. When done thoughtfully, these suggestions feel useful rather than pushy.
Customers are more likely to engage when they see recommendations that match their needs. Relevance builds trust and reduces decision fatigue.
Example: “Customers who bought this also added priority onboarding.”
9. Social proof-based and service upselling
Social proof-based upselling strategies uses reviews, ratings, or real usage data to reduce uncertainty. Customers trust other customers more than marketing claims.
Service upsells, such as extended support or warranties, work well when buyers want security. These Upselling Techniques succeed because they lower perceived risk.
Example: “Trusted by 5,000 users who upgraded to premium support.”
Psychology at work: Social validation reassures buyers they are making a good choice. Relevance bias keeps attention focused. Risk reduction removes one of the biggest barriers to upselling.
Real-Life Examples of Upselling Techniques
1. Fast-food combo upgrades
You order a burger, and the cashier asks if you want to make it a meal for a little extra. You were already buying the burger, so the upgrade feels easy. The value is clear and the decision takes seconds. This is a classic example of building on decision momentum, a principle that also applies to promotions on digital signage for restaurants.
Upselling Techniques used: Product upgrade with low friction.
2. Airline seat and baggage upgrades
After booking a flight, airlines offer seat upgrades, extra legroom, or additional baggage. The trip is already confirmed, so the upsell feels like improving comfort rather than making a new purchase. Timing is everything here.
Upselling Techniques used: Post-purchase upselling strategy and experience-based upselling.
3. Coffee size upgrade at a café
You order a regular coffee and hear, “For a small extra cost, you can get a large.” The price difference feels minor compared to the benefit.

[Image Source: Databox]
Upselling Techniques used: Tiered pricing and price relativity.
4. Movie theater snacks and combos
At the counter, popcorn and drink combos are priced to make the bundle look like the better deal. Buying items together feels smarter than choosing individually.
The bundle also reduces the effort of deciding.
Upselling Techniques used: Bundling and perceived savings.
5. Retail store warranties and protection plans
When buying electronics, stores often offer extended warranties or protection plans.
Customers are not buying features, they are buying peace of mind. This upsell works because it reduces fear of future problems.
Upselling Techniques used: Service upselling and risk reduction.
6. Gym membership tiers
Gyms usually show multiple plans, from basic access to premium memberships with personal training or classes. Most people choose the middle or higher option because it feels balanced. The comparison drives the decision.
Upselling Techniques used: Tiered pricing and anchoring.
Conclusion
Upselling Techniques work best when they respect how people actually make decisions. Real-life examples show that successful upsells do not rely on pressure or aggressive tactics. They rely on timing, relevance, and clarity. Whether it is upgrading a coffee size, adding baggage to a flight, or choosing a better seat at a hotel, the upsell feels natural because it improves the experience.
The most effective Upselling Techniques build on intent instead of interrupting it. They reduce effort, frame value clearly, and remove uncertainty at the right moment. When customers understand why an upgrade makes sense, they feel confident saying yes. Over time, this approach increases average order value while keeping trust intact.
In short, upselling works when it feels like guidance, not persuasion. If your upsells mirror real-world buying moments and focus on genuine value, customers will see them as helpful choices rather than extra costs.








What i don’t understood is in fact how you are now not actually a lot more smartly-favored than you may be right now. You are so intelligent. You understand thus significantly with regards to this matter, made me individually believe it from a lot of varied angles.